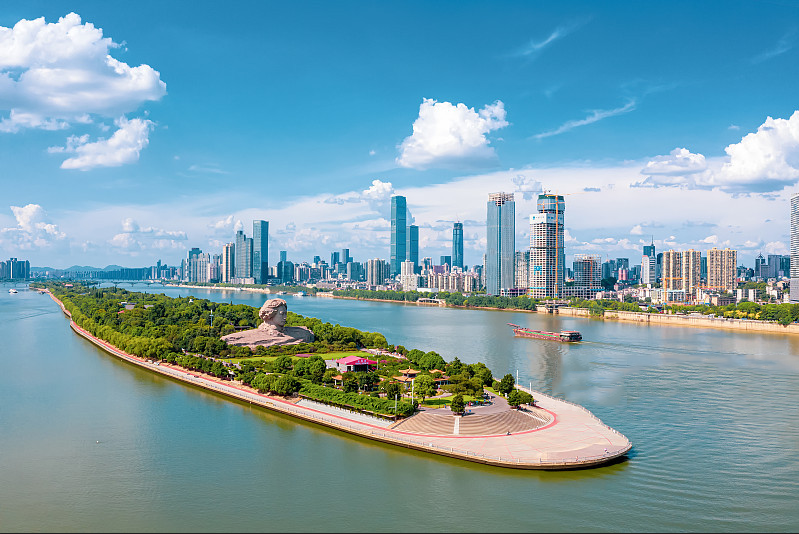
Changsha is the capital of Hunan Province in the People’s Republic of China. It is an important central city in central China and one of the megacities in China, with a population of over ten million, the important central city in the middle reaches of the Changjiang River.
Changsha is an important central city in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, a national “two-oriented society” comprehensive supporting reform pilot area, an important grain production base in China, and an important node city in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River city cluster and the Yangtze River Economic Belt. It is adjacent to Yichun and Pingxiang of Jiangxi Province in the east, Loudi and Yiyang in the west, Zhuzhou, and Xiangtan in the south and Yueyang in the north. Changsha is a comprehensive transportation hub where Beijing-Guangzhou high-speed railway, Shanghai-Kunming high-speed railway and Chongqing-Xiamen high-speed railway converge. With Yuelu Mountain, Xiangjiang River and Orange Island as geographical and cultural symbols, Changsha is also known as the “City of Mountains and Rivers”. It is also known as the “Capital of Entertainment” in China because it has nurtured the city culture of both elegance and folklore.
Changsha is one of the first national historical and cultural cities, after three thousand years of city name, city site unchanged, “Qu Jia town”, “Chu Han city”, “Xiao Xiang Zhu Si” said. There are historical relics such as Mawangdui Han Tomb, Four Yang Square statue, three Kingdoms Wu Jian, Yuelu Academy and Tongguan Kiln. The Huxiang culture of “applying to the world and being inclusive” is condensed.
Changsha traditionally takes construction machinery manufacturing as a pillar industry. With the economic transformation, the output value of new materials industry reached 262.1 billion yuan in 2015, replacing construction machinery to become the largest industry in Changsha. In 1978, the total GDP of Changsha was 1.685 billion yuan, and reached 1,053.551 billion yuan in 2017. Changsha, which once had a weak foundation, accelerated industrialization by promoting independent innovation and focused on strengthening the county economy, and its GDP increased by 460% from 2005 to 2015, ranking first among thirty-three major cities. In 2016, Changsha put forward the goal of building “three centers”, namely the National intelligent Manufacturing Center, the National Innovation and Creativity center, and the national transportation and logistics center. There are fifty-eight universities in Changsha, 97 independent research institutes, 52 academicians, 14 national engineering technology research centers and 15 national key engineering laboratories. There are scientific achievements such as hybrid rice breeding, “Tianhe” supercomputer, and the first 3D sintering printer in China.